What Other Name Is Used to Describe Oxidative Phosphorylation
-has catalytic activity of enzyme and retains this activity. It is also the method used in the light reactions of photosynthesis to harness the energy of sunlight in the process of photophosphorylation.
7 4b Chemiosmosis And Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Libretexts
Historically bovine heart mitochondria have been the system of choice for the structural characterization of eukaryotic OXPHOS complexes Saraste 1999 because.

. Describe the Fo subunit of ATP synthase. Identify the phases of cellular. In chloroplasts this process is often referred to as the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Describe the mechanism of ATP synthesis. Oxidative phosphorylation consists of two elements. It occurs in the mitochondria.
The flowing of the proton through the Fo subunit causes the component in the matrix FI to synthesize ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation can be broken down into two parts. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process where energy is harnessed through a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner-membrane of mitochondria called the electron transport chain and ATP synthase to create ATP.
Up to 24 cash back Oxidative Phosphorylation 5 Extension Questions 17. Describe the use of Uncouplers in elucidating the mechanism of ATP synthesis. The potential energy of this gradient is used to generate ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the term used. Descirbe the F1 subunit of ATP synthase. The electron transport system is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
As the protons build up they create a proton-motive force. Oxidative phosphorylation is the final step in cellular respiration. Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
Photosynthesis will be described in the next tutorial. In the electron transport chain electrons are passed from one carrier to another forming an electrochemical gradient that can be used to power oxidative phosphorylation Chemiosmosis describes the formation of ATP using this gradient. The process of oxidative.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the term used for the attachment of free inorganic phosphate to a molecule. Substrate level phosphorylation is the term used for phosphorylation that removes a phosphate from one molecule and joins it to another molecule. Chemiosmosis is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism.
Adenosine Tri-Phosphate is an important factor for the survival and function of living organismsATP is known as the universal energy currency of the life. This tutorial will describe oxidative phosphorylation in detail. In mitochondria this process is the final stage of cellular respiration and is referred to as oxidative phosphorylation.
Adenosine triphosphate is the major product of oxidative phosphorylation as it is the premier energy molecule of the cell. The ability to convert the energy from food. The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Key Difference Oxidative phosphorylation vs Photophosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is the sequence of reactions in mitochondria that convert energy from food into cellular energy by synthesizing ATP the primary energy currency of cells. Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components.
It is linked to a process known as electron transport chain. In chemiosmosis the energy stored in the. The Electron Transport Chain.
The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. Up to 24 cash back Substrate level phosphorylation is the term used for phosphorylation that removes a phosphate from one molecule and joins it to another molecule. The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
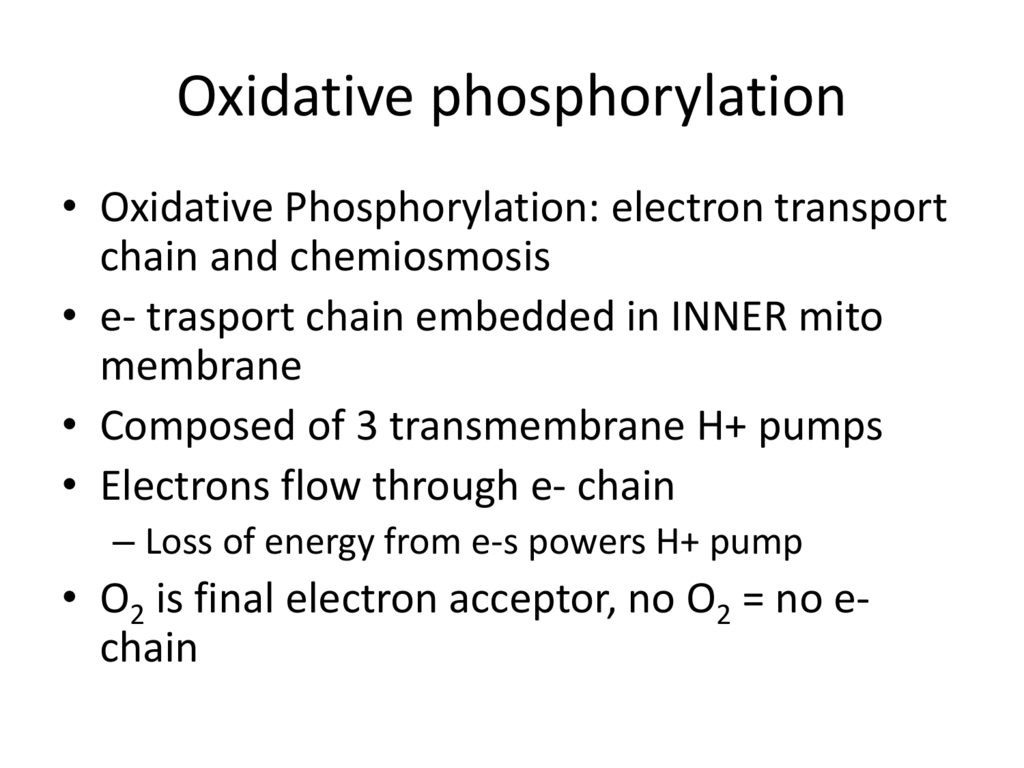
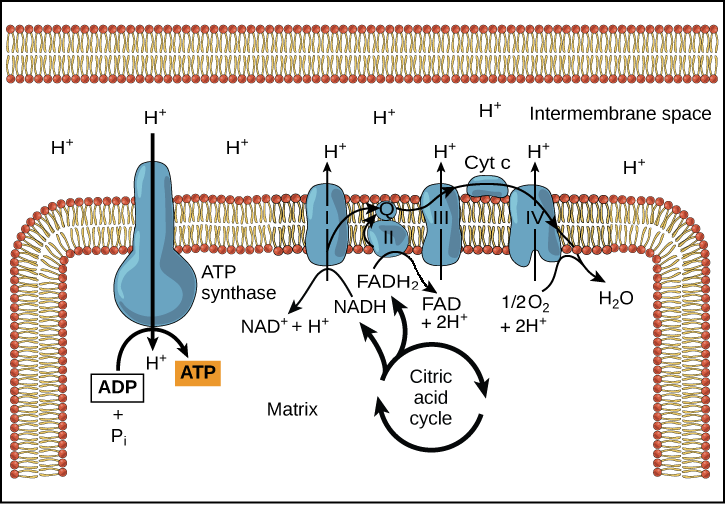
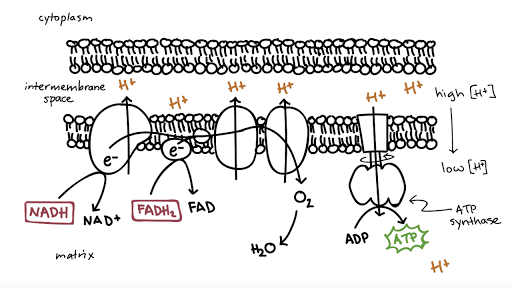
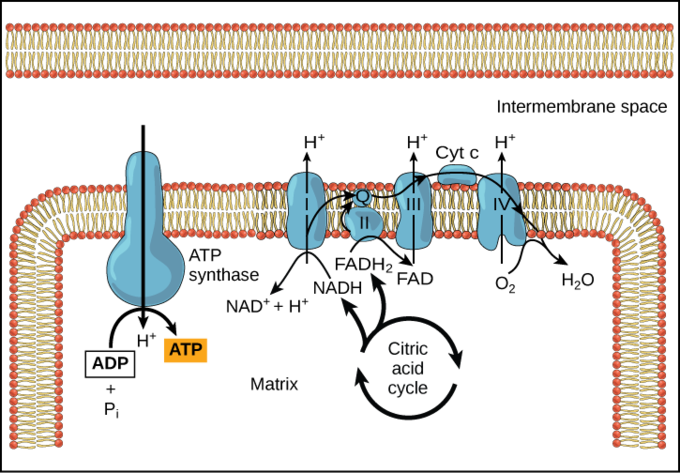
Oxidative phosphorylation is a process involving a flow of electrons through the electron transport chain a series of proteins and electron carriers within the mitochondrial membrane. The electron transport chain Figure 2 a is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. -contains 5 different subunits and protrudes into the mitochondrial matrix.
To drive the second step in oxidative phosphorylation electrons must be passed to one of the electron carrier molecules of the electron transport system. As many of you know creating usable energy is one of the most important functions of nearly every cell in the. Identify the statements that accurately describe how hydrogen ion concentration relates to energy production in oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the term used for the attachment of free inorganic phosphate to a molecule. Oxidative phosphorylation OXPHOS is defined as an electron transfer chain driven by substrate oxidation that is coupled to the synthesis of ATP through an electrochemical transmembrane gradient Figure 131. The entirety of this process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the term used for the attachment of free inorganic phosphate to a molecule. Distinguish substrate level phosphorylation from oxidative phosphorylation. During oxidative phosphorylation electrons derived from NADH and FADH 2 combine with O 2 and the energy released from these oxidation reduction reactions is used to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADPThe transfer of electrons from NADH to O 2 is a very energy-yielding reaction with ΔG -525 kcalmol for each pair of electrons transferred.
Mitochondrial matrix cytoplasm and inner mitchondrial membrane. In the electron transport chain electrons are passed from one molecule to another and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient. Production of ATP within the living system occurs in many ways.
Substrate level phosphorylation is the term used for phosphorylation that removes a phosphate from one molecule and joins it to another molecule. The electrons are transferred from one member of the transport chain to another through a series of redox reactions. Yield of ATP moles per mole of NADHH oxidized by the electron transport chain.
By definition oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 molecules through a series of electron carriersprotein complexes in order to generate ATP from ADP for the cells energetic needs. This flow of electrons allows the electron transport chain to pump protons to one side of the mitochondrial membrane. 1 Oxidation of NADH and FADH and 2 Phosphorylation.
Substrate level phosphorylation is the term used for phosphorylation that removes a phosphate from one molecule and joins it to another molecule.
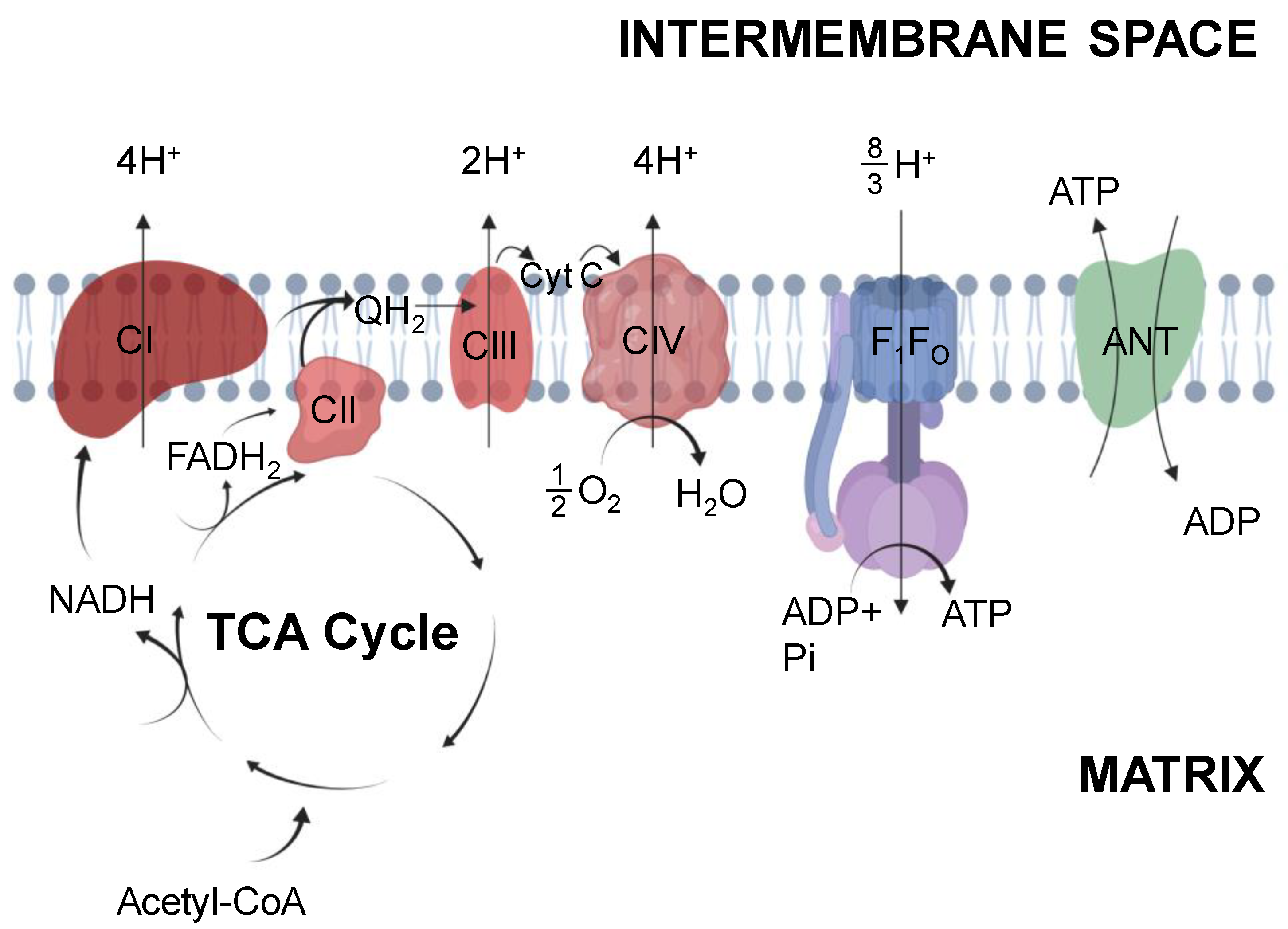
Ijms Free Full Text Quantification Of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation In Metabolic Disease Application To Type 2 Diabetes Html
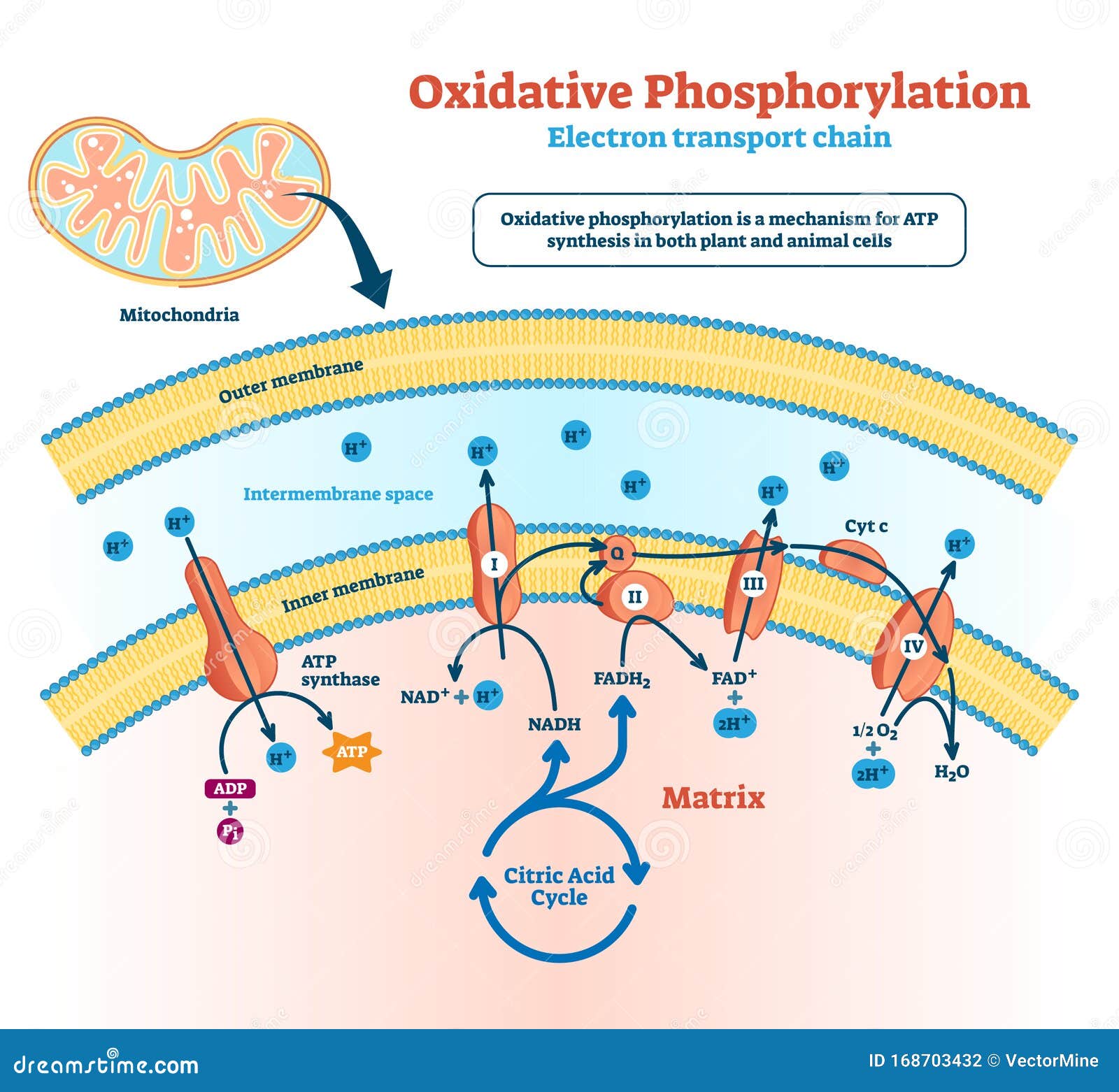
Oxidative Phosphorylation Stock Illustrations 51 Oxidative Phosphorylation Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime

Lesson Explainer Oxidative Phosphorylation Nagwa
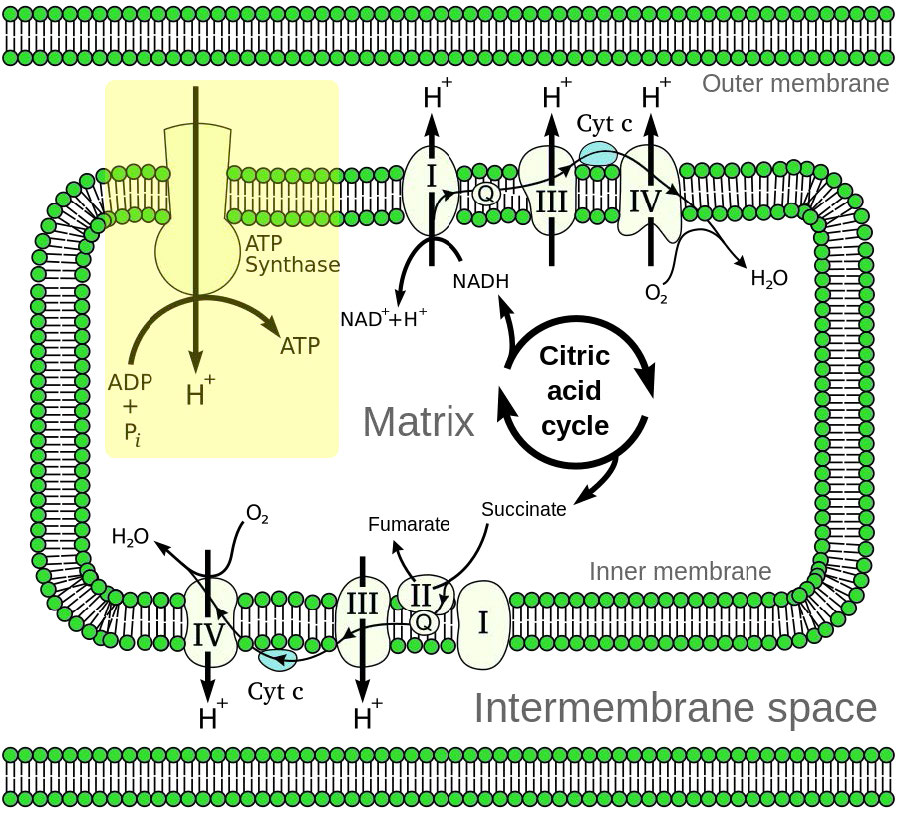
5 2 Electron Transport And Oxidative Phosphorylation Introductory Biochemistry
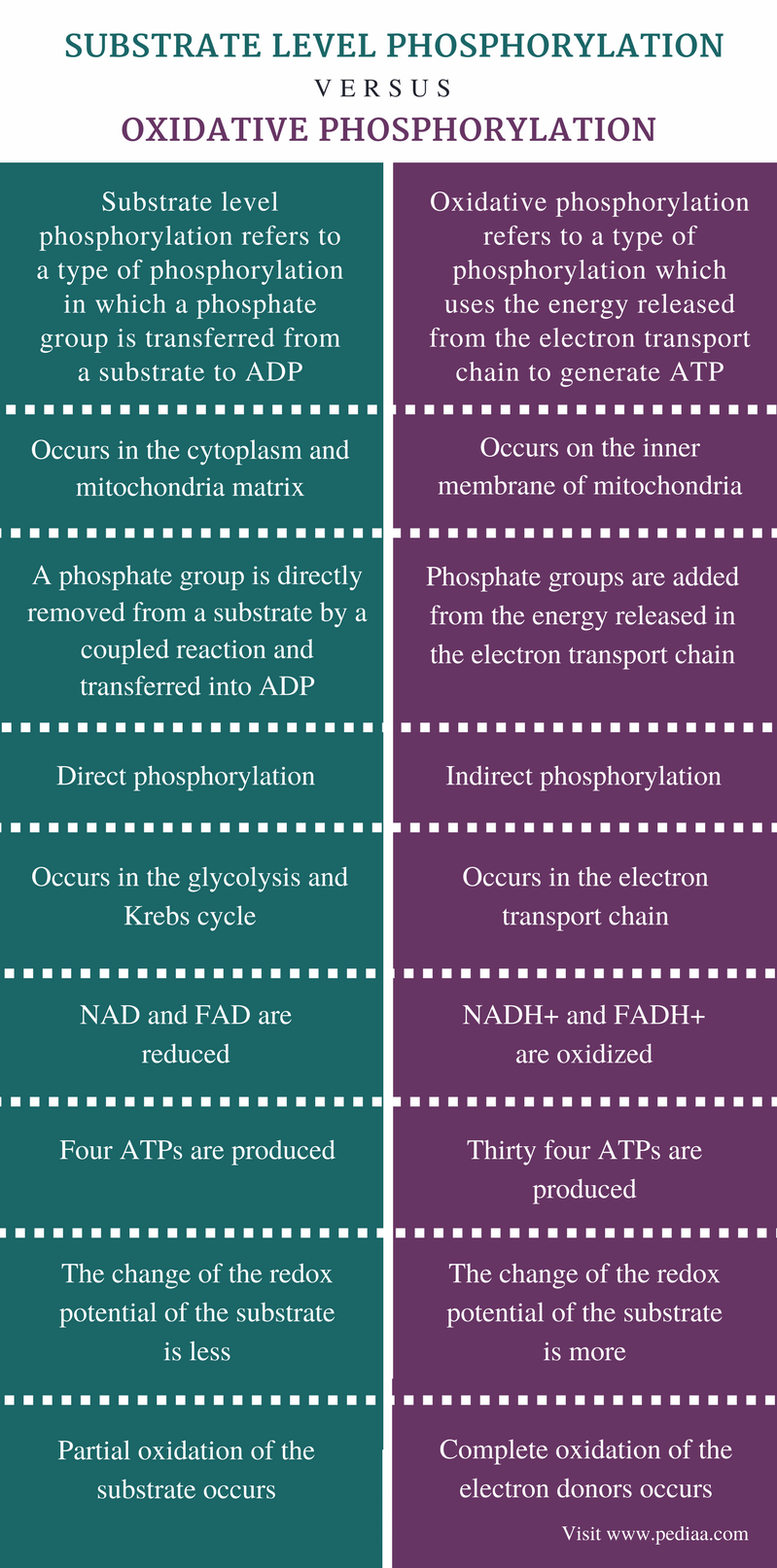
Difference Between Substrate Level Phosphorylation And Oxidative Phosphorylation

Question Video Describing The Process Of Oxidative Phosphorylation Nagwa
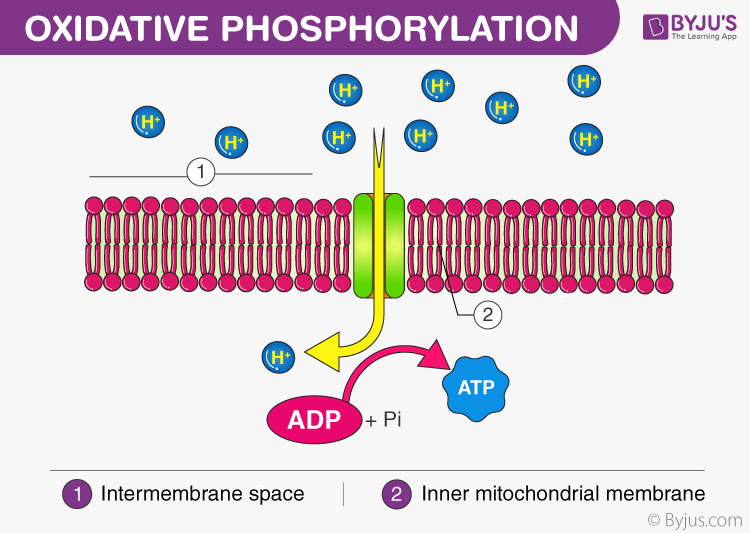
Oxidative Phosphorylation Definition Oxidative Phosphorylation Steps

Uncoupling Process Of Uncoupling Of Oxidative Phosphorylation In Download Scientific Diagram

Oxidative Phosphorylation In Mitochondria The Oxidation Of Energy Download Scientific Diagram

Summary Of Oxidative Phosphorylation Download Scientific Diagram
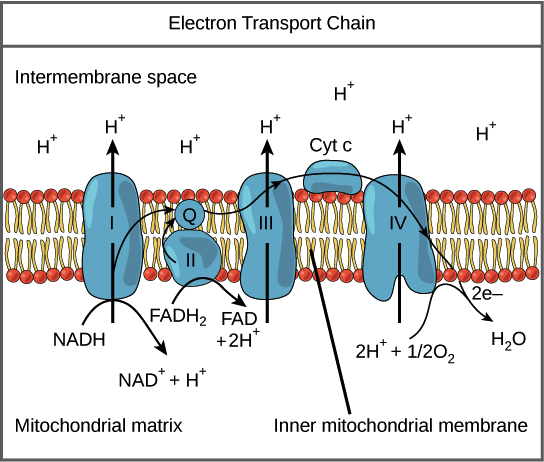
Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy

Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation Substrates And Products General Features Of The Pathway Oxidative Phosphorylation Mcat Content
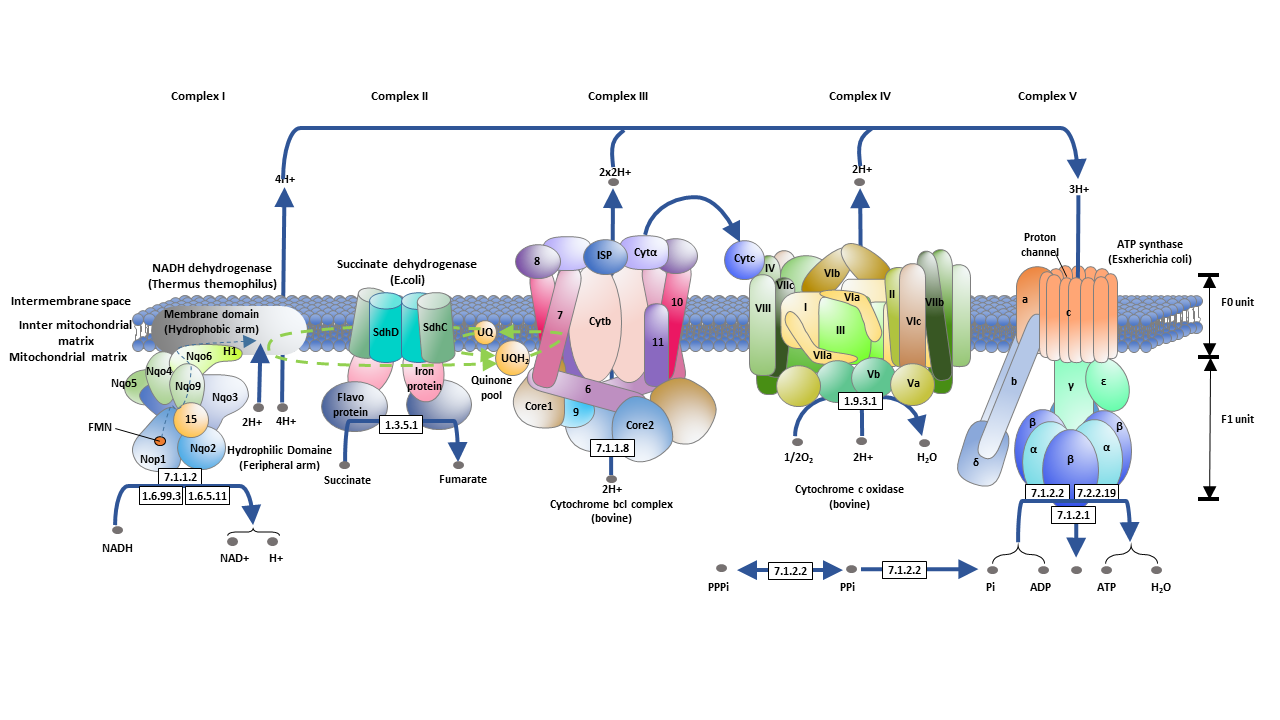
Oxidative Phosphorylation Cusabio

Oxidative Phosphorylation Definition Steps A Level Biology Revision

Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Dictionary
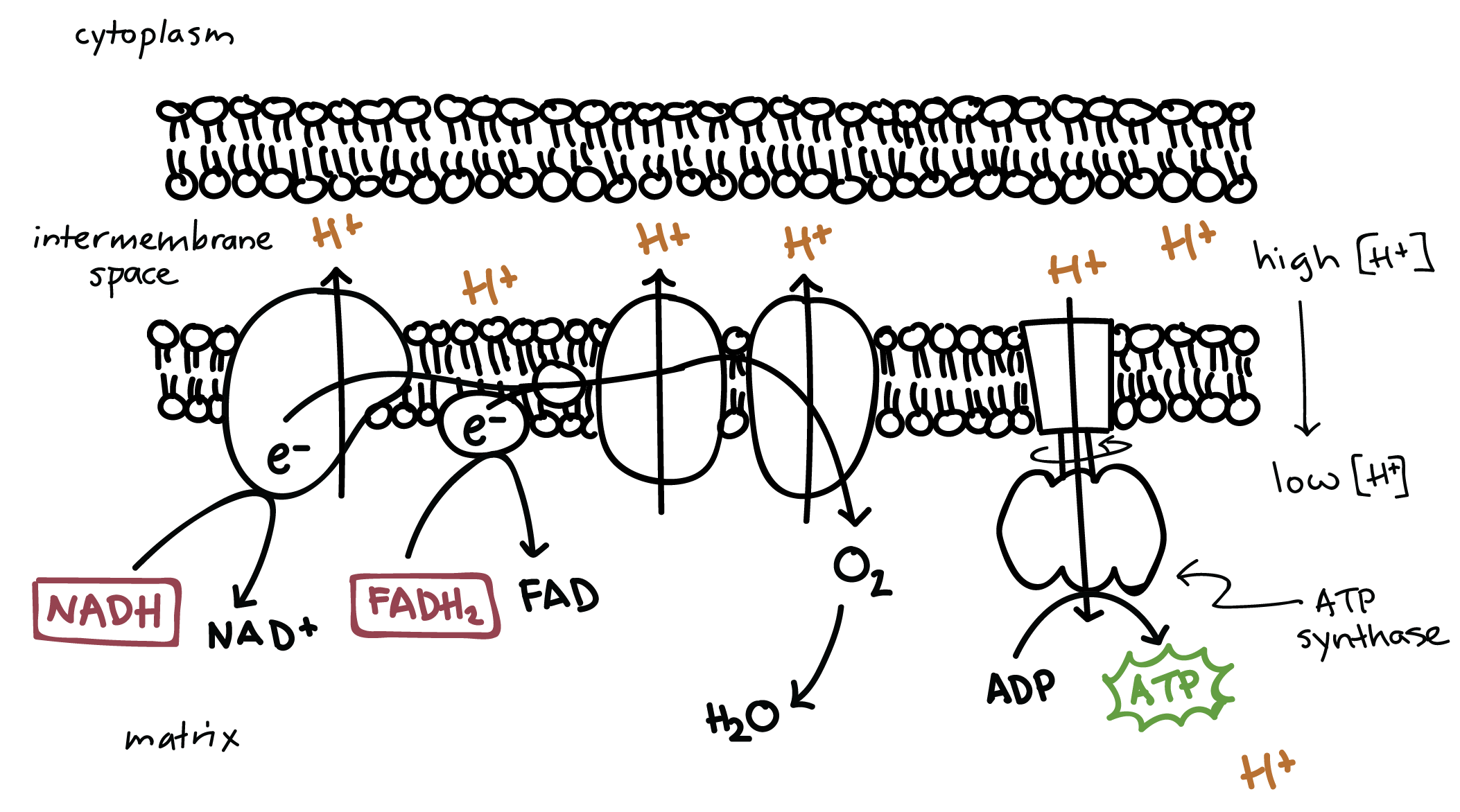
Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy